Backward Design Center for the Advancement of Teaching Excellence University of Illinois Chicago
Table Of Content
- Basic Steps of Backward Design Lesson Plans
- Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction
- Alignment of learning objectives to learning activities
- Backward Design Model: Lesson Plans and Examples [PLUS: Free Lesson Plan Template]
- QUESTIONS TO ASK BEFORE SELECTING A CURRICULUM DESIGN COURSE
- How Can We Align Learning Objectives, Instructional Strategies, and Assessments?
- I. Identify the desired outcomes

In choosing the strategies for your course, then, it is important to consider the levels of thinking, understanding, and reasoning that will best serve your desired learning goals for the course. For example, in preparing lessons on Speaking and Listening, in the Common Core. A teacher should ask himself, what will count as evidence of learning?
Basic Steps of Backward Design Lesson Plans
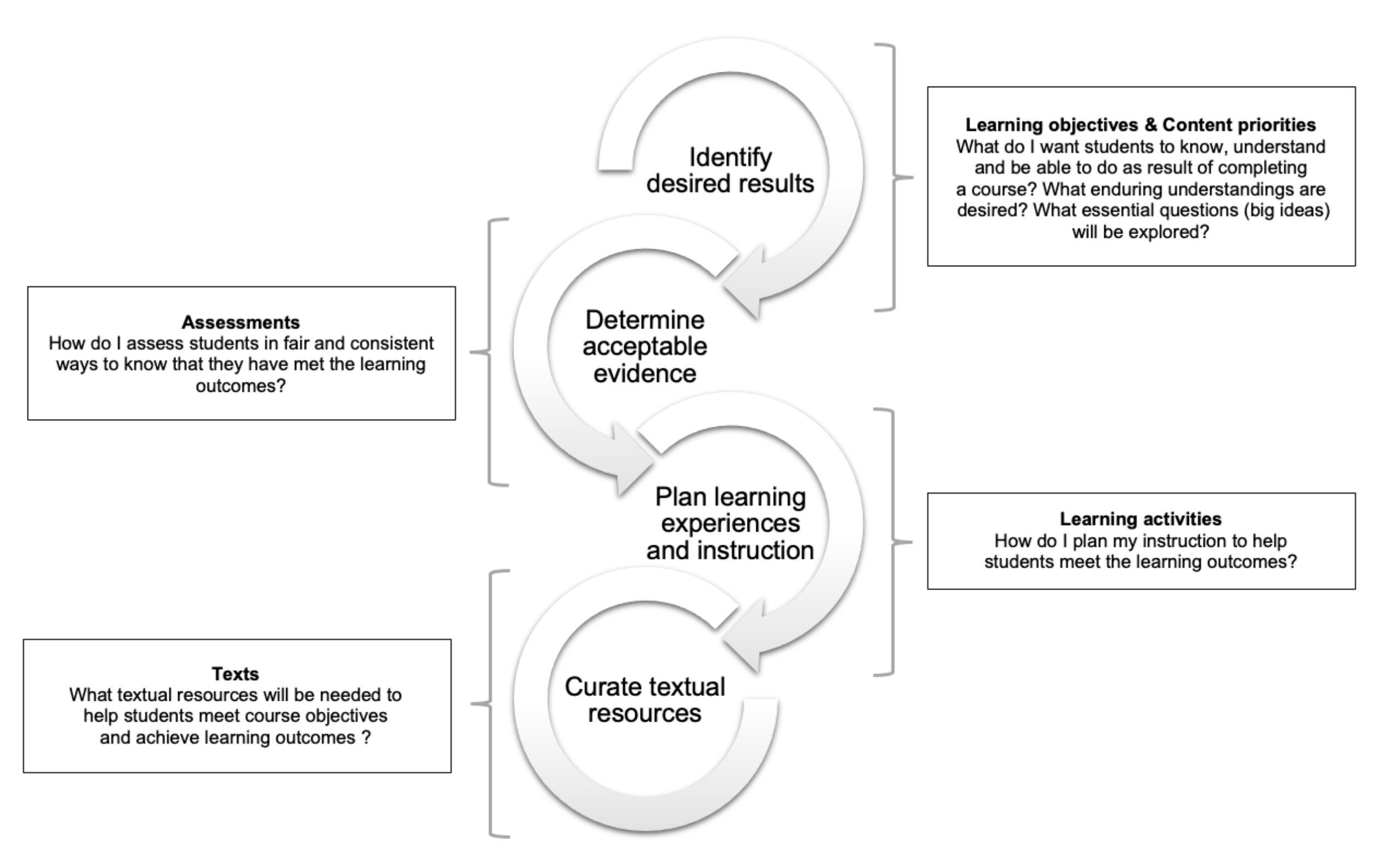
Wiggins and McTighe have created a six-part checklist built on the acronym WHERETO that consists of key elements that should be included in your instructional materials and learning activities. Assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students. Do students need to know this to succeed in obtaining the core concepts and competencies? By creating a curated framework, instructors can teach students how to learn in the discipline rather than focusing on content coverage (Peterson et al. 2020). In other words, a superior education will teach students to think and practice like scientists. If we don’t plan learning experiences that make that possible, we’re giving them a sub-par education.
Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction
Although backward design is based on the same components of the ADDIE model, backward design is a condensed version of these components with far less flexibility. Backward design arose in tandem with the concept of learning standards, and it is widely viewed as a practical process for using standards to guide the development of a course, unit, or other learning experience. Like backward designs, learning standards are a way to promote greater consistency and commonality in what gets taught to students from state to state, school to school, grade to grade, and teacher to teacher. We suggest that the Backward Design framework (Wiggins and McTighe, 2005) represents a more effective approach to both course design and redesign, and is appropriate regardless of whether the course takes the form of a lecture, discussion, or lab.
Three Reasons to Consider Bulk Lesson Planning - Inside Higher Ed
Three Reasons to Consider Bulk Lesson Planning.
Posted: Thu, 05 Jan 2017 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Alignment of learning objectives to learning activities
Learning outcomes and/or objectives should target complex skills and knowledge, by implementing Bloom's terminology into a learning outcome instructors can help students understand what they need to do in order to meet the desired results. How will students be able to know they have succeeded in learning the core concepts and competencies? Consider various forms of both formative and summative assessment (see more in the assessment tab below). Furthermore, when a teacher designs a lesson without a plan for the final assessment, they may be tempted to add activities or units to the lesson just for the sake of filling class time. Students of all ages know when they are asked to do something pointless in class; they can spot “busy work” from a mile away, and will disengage as they see fit.
Students with Special Needs Archives - eSchool News
Students with Special Needs Archives.
Posted: Tue, 06 Dec 2022 13:54:04 GMT [source]
Backward Design Model: Lesson Plans and Examples [PLUS: Free Lesson Plan Template]
This fully online program is for anyone developing and/or teaching an online course.ADDIE Instructional Design Certificate Program (Fully Online). This fully online program is designed for individuals interested in learning more about the ADDIE model.Instructional Design Models Certificate (Fully Online). You will explore traditional instructional design models and the progression of the learning design approach to creating online learning experiences. The primary starting point for backward design is to become familiar with the standards/outcomes for the grade level and curriculum being taught. The second part of curriculum planning with backward design is finding appropriate assessments. It can be difficult for "traditional" educators to switch to this model because it is hard to conceptualize an assessment before deciding on lessons and instruction.
QUESTIONS TO ASK BEFORE SELECTING A CURRICULUM DESIGN COURSE
You’ll want to utilize explicit instruction, such as a Y chart (looks like, feels like, sounds like) for each skill. Just as you would in your lessons, create authentic opportunities to engage with the skill, provide feedback to students on their progress with the skill, and make time to directly connect lessons and activities to the skill you’re working on. On the other hand, if one of your important goals is to help students develop their ability to master mechanical tools, a problem-solving test may not provide you with the type of evidence of progress that you require. Whatever the case may be, there is an alternative approach that helps instructors avoid these pitfalls and mitigate student frustrations with their learning experiences. Backward design takes a learner-centered approach to course design, facilitating the creation of more cohesive, clear, and intentional learning experiences for students. A learner-centered approach goes beyond engaging students in content and works to ensure that students have the resources and scaffolding necessary to fully understand the lesson, module, or course.
Explore education courses and certificates at the University of San Diego’s Division of Professional and Continuing Education. With this “after” version, every lesson is designed to prepare students to give excellent presentations at the end. The whole time, they are using the lunar cycle vocabulary, correcting each other’s misconceptions, and just like scientists, thinking about how to explain concepts to other people. With a good rubric in place, we then work backwards to determine what lessons students need to do excellent work on the final assessment.
The Derek Bok Center for Teaching and Learning
In addition, it is helpful to ask yourself what the impact of the course will be on students, and how you hope they will be different by the end of it. In order for students to demonstrate whether they've accomplished the objective we set, the paper they write or the exam they take has to evaluate that objective specifically. Both the form and content of the assessment can facilitate (or hinder) that evaluation. Asking students to provide dates of battles, names of generals, and pre-war compromises assesses recall of facts, but not analysis or argumentation. Similarly, a multiple choice format that asks students to pick the most important cause of the war out of a set of four fails to provide the opportunity for in-depth comparison. Our first sample objective from above, for example, is probably best assessed through an essay format, one that asks students to compare more and less important causes of the Civil War.
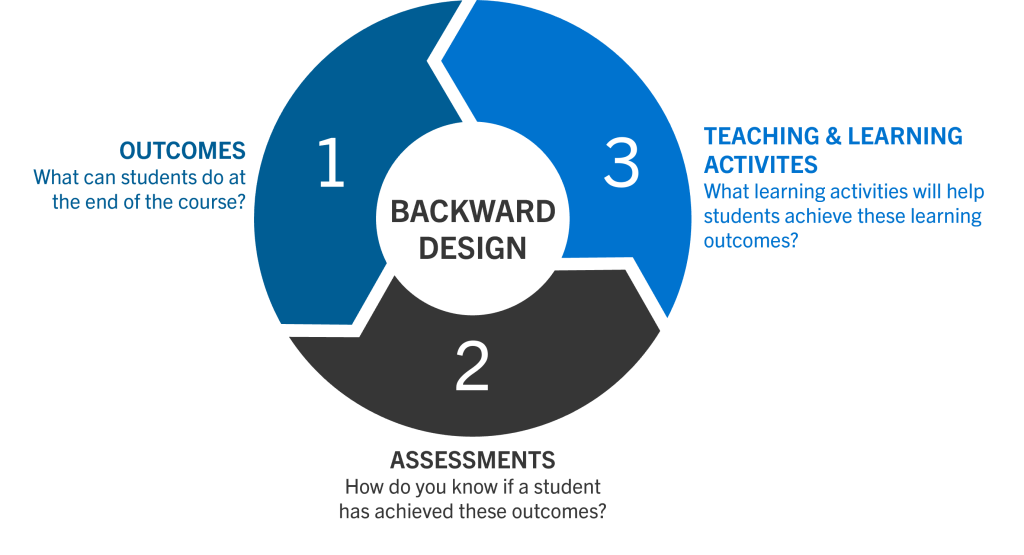
I. Identify the desired outcomes
A downloadable guide for teaching professionals from the University of San Diego. Enduring ideas and opportunities for authentic, discipline-based work. Browse over 500+ educator courses and numerous certificates to enhance your curriculum and earn credit toward salary advancement. Instead of starting with a topic, we’d do better if we start with an end goal, and that’s where backward design comes in.
Wiggins and McTighe identify a link between the assessment format and the type of understanding students need to demonstrate. For example, if the goal is for students to learn basic facts and skills, traditional quizzes and tests might be the most appropriate type of assessment to use. However, when the goal is enduring understanding, more complex and authentic assessment strategies might be needed to assess student learning.
We can leverage backward design and other best practices in pedagogy to provide our students with rich learning experiences that support all of their needs. A formative assessment does not look backwards but it focuses on the present of where the student is right now, it looks to the future. Summative means there is no opportunity to "re-do", it is for real, like the championship game.
What do you want students to know or be able to do at the end — explain how cells work? Backward lesson design begins with identifying a specific desired outcome. Notice that in this approach, the assessment is created after the lessons are planned. Sometimes it isn’t created until most of those lessons have already taken place.
By answering the three questions presented at this stage, instructors will be able to determine the best content for the course. Furthermore, the answers to question #3 regarding enduring understandings can be adapted to form concrete, specific learning goals for the students; thus, identifying the desired results that instructors want their students to achieve. Traditionally, instructors have applied a forward or content-centered approach to designing lessons, modules, or courses. This approach typically ends with crafting learning objectives to connect the content learned to the assessments. Backward design helps teachers create courses and units that are focused on the goal (learning) rather than the process (teaching). Because “beginning with the end” is often a counterintuitive process, backward design gives educators a structure they can follow when creating a curriculum and planning their instructional process.
Once we've designed an assessment, our final task—which brings us around to the "front" of Backward Design—is to plan our teaching, which should enable students to complete the assessment successfully, thereby demonstrating their learning. Lecturing, primary and secondary readings, student presentations, and debates are all possible ways of structuring student learning towards the eventual assessment. There are merits to both traditional lesson planning and backward lesson design, but key differences can create challenges for some teachers and students.
It would be easy to blow off this distinction, to say Bah, same difference. The test asks students a lot of questions that would show an understanding of these concepts, so we’re covered. The first and most important problem is a lack of durable, transferable learning.
Comments
Post a Comment